Use the New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet in PowerShell to create a self-signed certificate for the IIS website in the LocalMachine\My store.
Self-Signed certificates are created for testing purposes, while creating the self-signed certificate requires CertStoreLocation, DNSName, FriendlyName, certificate start date, and expiry date. Certain properties are optional while creating a self-signed certificate.
In this article, we will discuss how to create a self-signed certificate with an expiry date of 1 year for the IIS website.
New-SelfSignedCertificate – Create Self-Signed Certificate IIS
Use the New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet available in the PKI module to create a self-signed certificate for the IIS website.
Run the following PowerShell script that makes use new-selfsignedcertificate cmdlet to create a certificate in MY store.
New-SelfSignedCertificate ` -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My ` -DnsName "localhost" ` -FriendlyName "HMITest" ` -NotAfter "01/12/2023" -Verbose
In the above PowerShell script, the New-SelfSignedCertificate uses the CertStoreLocation parameter to specify the certificate store LocalMachine\My to store the new certificate.
The DnsName parameter of New-SelfSignedCertificate is used to specify one or more DNS names to put into the subject alternative name.
The FriendlyName parameter of New-SelfSignedCertificate is used to specify a friendly name for the new certificate.
NotAfter parameter of New-SelfSignedCertificate is used to specify an expiration date for the new certificate.
The output of the above PowerShell script creates a new certificate “HMITest” and stores it in LocalMachine\My cert store with an expiry date as 01/12/2023.
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> New-SelfSignedCertificate `
-CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My `
-DnsName "localhost" `
-FriendlyName "HMITest" `
-NotAfter "01/12/2023" -Verbose
VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Create a new self-signed certificate" on target "Cert:\LocalMachine\My".
PSParentPath: Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate::LocalMachine\My
Thumbprint Subject
---------- -------
88BBB210E2F12DAA9D38AF8254E528F1F3886C7A CN=localhost Use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet in PowerShell to check if the certificate exists in the cert store or not.
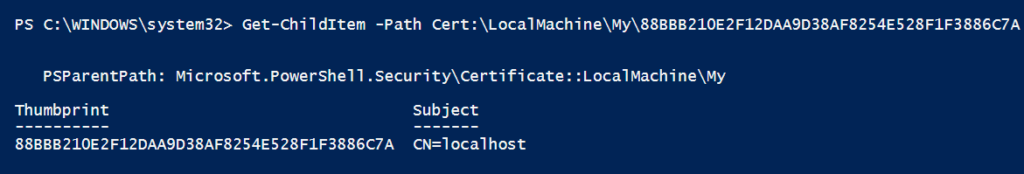
Run the following PowerShell script that checks if the newly created self-signed certificate is available in the LocalMachine\My store or not.
Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\My\88BBB210E2F12DAA9D38AF8254E528F1F3886C7A
The Get-ChildItem cmdlet uses the Path parameter to specify the cert:\ store location path and retrieve the certificate details by thumbprint.
The output of the above PowerShell script gets the certificate details as given below:
Cool Tip: How to bind an SSL certificate to the IIS site in PowerShell!
Conclusion
I hope the above article on how to create a self-signed certificate in PowerShell is helpful to you.
You can find more topics about PowerShell Active Directory commands and PowerShell basics on the ShellGeek home page.